In our modern lives, the internet plays an integral role. We rely on it for communication, work, entertainment, financial transactions, etc. However, this dependence also exposes us to a rising danger- cyber attacks. Cybercriminals are becoming more sophisticated and relentless, targeting individuals, businesses, and governments worldwide. The consequences of these attacks can be devastating, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and even national security threats. Utilizing comprehensive cyber security services is crucial to counter these threats effectively.
Understanding the nature of cyber attacks and how to defend against them is crucial for anyone using the internet. This detailed guide aims to simplify the complex world of cybersecurity by exploring various types of cyber attacks and offering practical strategies to protect yourself and your organization. Whether you are an individual concerned about your data, a business owner aiming to safeguard your assets, or a government official tasked with securing critical infrastructure, this guide will provide valuable insights and actionable advice.
From phishing and ransomware to more advanced threats like SQL injection and man-in-the-middle attacks, Cyber attacks come in many forms. Each type of attack exploits different vulnerabilities and can have unique consequences. By understanding these threats and staying informed about the latest trends in cybercrime, you can better protect your digital life. With the help of a professional cyber security services provider, one can maintain a strong security posture. This guide also highlights the importance of adopting proactive security measures, from strong passwords to regular software updates, to mitigate the risk of Cyber attacks. Let’s explore the field of cybersecurity and prepare ourselves with the knowledge to stay safe online.
What is a Cyber Attack?
A cyberattack is any unauthorized attempt to access a computer, system, network, or device, with malicious intent. These cyber attacks can take various forms, including data breaches, malware infections, and denial-of-service attacks. The motives behind cyber attacks are diverse and can range from data theft and operational disruption to installing malicious software or launching additional attacks. Cybercriminals may target individuals, businesses, governments, or critical infrastructure, depending on their goals and the potential impact of the attack. Cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving, making it crucial for organizations to stay vigilant.
Here are some of the most common goals of cyber attacks:
- Data theft
Attackers may steal sensitive information such as personal data (names, addresses, social security numbers), financial data (credit card numbers, bank account details), or intellectual property (trade secrets, research data). This stolen data can be used for identity theft, financial fraud, or sold on the dark web. Data breaches can have severe consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions for the affected organizations. Cybersecurity threats related to data theft are particularly concerning for businesses.
- Disruption
In this significant goal of Cyberattacks, attackers may deploy malware or flood systems with excessive traffic in a Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack, rendering them inoperable. Cyber security attacks aimed at disruption can lead to significant downtime, loss of productivity, and financial losses. In some cases, attackers may target critical infrastructure, such as power grids, transportation systems, or healthcare facilities, to cause widespread disruption and chaos.
- Financial Gain
Cybercriminals may use stolen data to commit fraud or hold systems hostage with ransomware, demanding a ransom payment to restore access. Ransomware attacks have become increasingly common and sophisticated, targeting businesses of all sizes and sectors. These attacks can cripple operations, leading to substantial financial losses and reputational damage. Financially motivated cyber security attacks are a major concern for organizations worldwide.
- Espionage
Governments, businesses, or individuals can be targeted to steal confidential information, such as classified documents, trade secrets, or intellectual property. This stolen information can be used for competitive advantage, blackmail, or furthering political agendas. State-sponsored cyber attacks are frequently driven by espionage goals, with attackers seeking to gain strategic or economic advantage over their adversaries.
How Often Do Cyber Attacks Occur?
Cyber attacks are a constant threat, happening around the world every day. The frequency and sophistication of attacks are on the rise. According to Security Magazine, there are over 2,200 attacks each day, breaking down to nearly 1 cyberattack every 39 seconds. This constant stream of attacks highlights the need for strong cybersecurity measures and ongoing vigilance.
The rise in Cyber attacks can be linked to several factors, including:

- Increased Reliance on Technology
As more aspects of our lives become digitized, the attack surface for cybercriminals expands. The increase in connected devices, from smartphones to smart home systems, creates more entry points for attackers. This interconnectedness, while convenient, also increases the risk of Cyber attacks, requiring strong security measures. Also, cybersecurity threats related to connected devices are a growing concern.
- Evolving Attack Techniques
Cybercriminals continuously develop new methods to exploit vulnerabilities and get around security measures. These techniques range from sophisticated malware and ransomware to social engineering tactics like phishing and spear-phishing. The fast changes in attack techniques make it challenging for individuals and organizations to keep up and defend against emerging threats. These emerging cybersecurity threats necessitate constant updates to security protocols.
- The Rise of Ransomware
Ransomware attacks have become a highly profitable business model for cybercriminals, further fueling the increase in cyber attacks. Cybersecurity threats from ransomware are particularly damaging. These attacks have become increasingly sophisticated, targeting both large corporations and small businesses. Attackers demand substantial ransom payments to restore access to encrypted data, causing significant financial losses and operational disruptions. The success of ransomware attacks has incentivized cybercriminals to launch more attacks, seeking to maximize their profits.
- Global Reach and Anonymity in Cyberspace
The global nature of the internet allows cybercriminals to operate from anywhere, making it challenging to trace and catch them. The anonymity provided by the digital world enables attackers to launch attacks with relative freedom, further fueling the rise in Cyber attacks. Understanding the frequency and causes of cyber attacks highlights the need for strong cybersecurity measures to protect against these constant threats. Cybersecurity threats being a global issue require international cooperation to address effectively.
Who Do Cybercriminals Target?
Anyone can be a target of a cyber attack, but some individuals and organizations are more at risk than others. Cybercriminals often target those who possess valuable data, have weaker security measures, or can be exploited for financial gain. Here are some of the most common targets:
Individuals
Cybercriminals frequently target individuals through phishing attacks, malware infections, and social engineering scams. These attacks often aim to steal personal information, such as social security numbers, bank account details, and login credentials. Cybercriminals may use this information for financial fraud, identity theft, or sell it on the dark web. Individuals who are not vigilant about their online security, such as using weak passwords or falling for phishing scams, are particularly vulnerable to cybersecurity threats.
Businesses
Regardless of the size, businesses are attractive targets for cybercriminals due to the valuable data they hold. Customer information, financial records, intellectual property, and trade secrets are prime targets for attackers seeking monetary gain. Cybersecurity threats to businesses are a growing concern, requiring strong defenses. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are particularly vulnerable, as they often lack the resources and expertise to implement strong cybersecurity measures. Cyber attacks on businesses can result in significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions.
Governments
Entities involved in national security and public services are frequent targets of Cyber attacks due to the sensitive information they possess. Cybersecurity threats to government entities can have far-reaching implications. Attackers may aim to disrupt essential services, steal classified information, or conduct espionage activities. State-sponsored cyber attacks are often politically motivated, seeking to gain strategic advantage or destabilize adversaries. To protect against these sophisticated threats, governments must invest in advanced cybersecurity technologies, establish collaboration with private sector experts, and create strong incident response plans.
Critical Infrastructure
Power grids, transportation systems, and healthcare facilities are prime targets for cyber attacks. Cybersecurity threats to these critical infrastructures can have severe consequences, affecting public safety, economic stability, and national security. This can cause widespread chaos, extort ransom payments, or further political agendas. Securing these vital systems requires resilient infrastructure, regular threat assessments, and public-private partnerships to mitigate the risks posed by cyber attacks.
Most Common Types of Cyber Attacks

Phishing
This deceptive tactic involves emails or messages that look like they come from legitimate sources, such as banks or social media platforms. These messages often create a sense of urgency or offer something that seems too good to be true, tricking victims into clicking on malicious links or revealing personal information. Phishing attacks are becoming more sophisticated, using advanced techniques like spear phishing, which targets specific individuals or organizations with tailored messages. To protect against phishing, individuals and organizations should be cautious of unsolicited messages, verify the sender’s authenticity, and use email filtering solutions to block malicious content.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
If someone were eavesdropping on a conversation, that’s sort of the idea with a Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack. An attacker will often position themselves between two people communicating online, intercepting data like passwords or credit card details. Public Wi-Fi networks are prime targets for these attacks. MitM attacks can compromise sensitive information and disrupt communication channels. To mitigate the risk of MitM attacks, individuals should avoid using public Wi-Fi for sensitive transactions, use virtual private networks (VPNs) to encrypt their communications, and enable HTTPS on websites to ensure secure connections.
SQL Injection
Websites rely on databases for storing information. SQL injection attacks exploit vulnerabilities in these databases by injecting malicious code into user inputs like search queries. This code can steal data or even manipulate the database itself. SQL injection attacks can have severe consequences, including data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information. Web developers can prevent SQL injection by using parameterized queries, implementing input validation, and regularly updating and patching database systems.
Ransomware
This cyber threat holds your information hostage. It encrypts your files, rendering them inaccessible, and then demands payment in the form of a ransom to decrypt them. Ransomware attacks can cripple both businesses and individuals, causing significant financial losses and operational disruptions. To protect against ransomware, it is essential to maintain regular data backups, implement strong security measures, and educate employees about the risks of suspicious emails and links.
Cryptojacking
In this attack, the attacker uses the processing power of your device for cryptocurrency mining. You may realize a significant slowing down of your computer, which is evidence of cryptojacking. This attack can go unnoticed for extended periods, causing damage to hardware and increasing energy consumption. To detect and prevent cryptojacking, individuals and organizations should monitor their device performance, use antivirus software, and block unauthorized mining scripts in web browsers.
DNS Tunneling
This technique involves hiding malicious traffic within seemingly harmless data streams like DNS requests. It’s like hiding a wolf in sheep’s clothing, making it difficult for security measures to detect the attack. DNS tunneling can be used to steal data, get around security controls, and establish persistent communication channels with compromised systems. To defend against DNS tunneling, organizations should implement advanced threat detection solutions, monitor DNS traffic for anomalies, and apply strict access controls on DNS servers.
URL Manipulation
Altering the parameters in a URL can allow attackers to gain unauthorized access to web applications or retrieve sensitive information. By manipulating URLs, attackers exploit vulnerabilities in the application’s logic, leading to data breaches and unauthorized actions. Web developers can prevent URL manipulation by validating and sanitizing user inputs, using secure coding practices, and implementing proper authentication and authorization mechanisms.
Password Attacks
Weak passwords are like open doors for attackers. Password attacks involve using automated tools to guess or crack passwords. Implementing strong, unique passwords for each online account is vital. Common password attacks include brute force attacks, dictionary attacks, and credential stuffing. To enhance password security, individuals and organizations should use complex passwords, enable multi-factor authentication, and regularly update passwords to mitigate the risk of unauthorized access.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Attacks
Websites often rely on user-generated content like comments. XSS attacks inject malicious scripts into this content. When another user views the content, the script can steal their information or hijack their session. XSS attacks can lead to data theft, unauthorized actions, and compromised user accounts. To prevent XSS attacks, web developers should sanitize and validate user inputs, use content security policies (CSP), and implement proper output encoding.
Insider Threats
Not all threats come from outside. Insider threats involve harmful actions by someone who already has authorized access to a system. Employees or individuals with legitimate access can misuse their privileges to launch attacks. Insider threats are a significant part of cybersecurity threats that organizations must address as they can lead to data breaches, intellectual property theft, and sabotage. To reduce the risk of insider threats, organizations should implement strict access controls, monitor user activity, conduct regular security audits, and promote a culture of security awareness and accountability.
Internet of Things (IoT) Attack
Smart devices like thermostats and home security cameras are convenient, but their security can be weak. Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in these devices to launch attacks on other devices or networks. IoT attacks can compromise privacy, disrupt services, and create entry points for larger cyber attacks. To secure IoT devices, individuals and organizations should change default passwords, regularly update firmware, and segment IoT devices from critical networks. Cybersecurity threats related to IoT devices are increasingly common as more devices become interconnected.
Spoofing
Impersonation is a key tactic in cyber attacks. Spoofing involves making a communication look like it comes from a trusted source, such as a bank or a colleague. This tricks victims into taking actions that compromise their security. Common spoofing attacks include email spoofing, IP spoofing, and website spoofing. To protect against spoofing, individuals and organizations should verify the authenticity of communications, use email authentication protocols, and educate users about the risks of spoofed messages. Understanding and mitigating these cybersecurity threats is crucial for maintaining security.
Malware Attack
Malicious software, or malware, includes various harmful programs like viruses, worms, Trojans, and spyware. These programs can steal data, disrupt operations, or even cause physical damage to devices. Malware can spread through email attachments, infected websites, and compromised software downloads. To protect against malware, individuals and organizations should use antivirus software, keep their software and operating systems up to date, and avoid downloading files from untrusted sources.
Web Attacks
Websites themselves can be targets. Web attacks exploit vulnerabilities in website software to inject malicious code, deface the website, or steal data from unsuspecting visitors. Common web attacks include SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and cross-site request forgery (CSRF). To protect websites, web developers should implement secure coding practices, use web application firewalls (WAF), and conduct regular security assessments and penetration testing.
Session Hijacking
This attack is like someone stealing your car while you’re momentarily distracted. Attackers steal a user’s session ID, which lets them impersonate the user and gain unauthorized access to their accounts. This type of attack can happen through various methods, including cross-site scripting (XSS) and man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks. The attacker can then act as if they were the legitimate user, leading to potential data breaches and other malicious activities. To protect against session hijacking, always use secure, encrypted connections (HTTPS) and regularly update your session management protocols.
Birthday Attack
A birthday attack takes advantage of weaknesses in cryptographic algorithms by finding collisions in hash functions, where two different inputs produce the same output. While not as common as other attacks, it shows why strong encryption methods are so important. The name comes from the birthday paradox in probability theory, which explains that collisions are more likely than we might expect. To reduce this risk, it’s crucial to use strong cryptographic algorithms and regularly update security protocols. Using modern cryptographic standards and increasing hash lengths can significantly lower the risk of birthday attacks.
Supply Chain
A supply chain attack is an attack where cyber-attackers focus on the vendors or suppliers of a company to just be able to get into the main company’s systems or information. This kind of attack exploits the interconnections that exist between businesses in a supply chain. Once they gain access, they have a breach into the network of the target. Such attacks can result in significant breaches and disruptions, underscoring the need for stringent security measures across the entire supply chain. Ensure comprehensive security assessments of all vendors and implement stringent access controls to protect against any supply chain attacks.
Trojans
The Trojans are, in essence, misleading programs. They appear to be genuine software, but they are armed with destructive codes. Through installations, they can aid in stealing data, downloading other forms of malware, and interfering with the operation of your system. Most frequently, trojans gain entry into a system through phishing emails or downloaded files. Unlike viruses, trojans do not self-replicate but can open doors for further attacks. These are always a severe threat, as they hide their malevolent intention until activated. Prevention and detection are required. Avoiding Trojans involves using good antivirus software, updating them regularly, and not downloading files from dubious sources.
DoS and DDoS Attack
A Denial of Service (DoS) attack attempts to flood a system with traffic from one source, making it unusable for regular users. A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack amplifies this by using many compromised devices to generate excessive traffic. These attacks overrun the resources of the targeted system, resulting in service outages. DDoS attacks are particularly damaging due to their scale and the difficulty in mitigating them, often requiring strong security measures. To protect against DoS and DDoS attacks, deploy a web application firewall (WAF) and use DDoS mitigation services.
Whale-phishing Attacks
Whale-phishing attacks specifically target high-ranking executives to access valuable company information. These individuals, often in the C-suite, are more likely to pay a ransom to protect their personal and organizational reputation. Attackers craft personalized and convincing emails to deceive executives into revealing sensitive information or transferring funds. Preventing such attacks involves educating executives about phishing tactics, implementing strong email security protocols, and using multi-factor authentication. Regular cybersecurity training and simulated phishing exercises can further help in safeguarding against whale-phishing attacks.
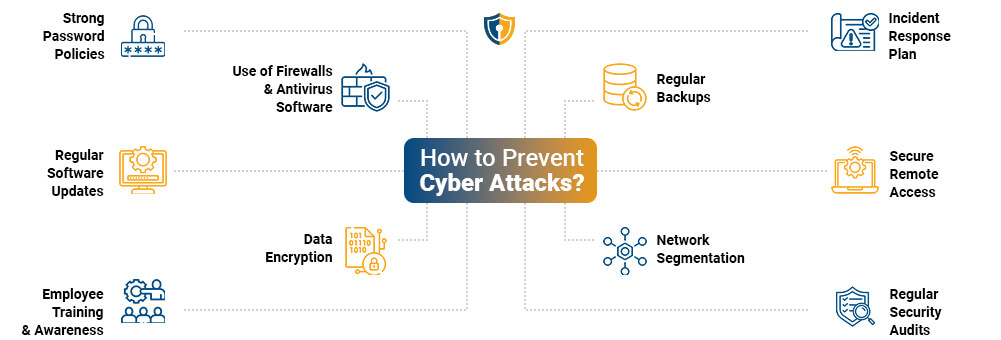
How to Prevent Cyber Attacks?
Preventing cyber-attacks requires a multi-layered approach that combines technology, best practices, and user awareness. Here are key strategies to enhance your cybersecurity posture:
-
Strong Password Policies
Implementing strong password policies is essential. Encourage the use of complex passwords that include a mix of letters, numbers, and special characters. Additionally, passwords should be changed regularly, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) should be enabled wherever possible. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring more than one form of verification to access accounts.
-
Regular Software Updates
Keeping your software and systems up-to-date is crucial. Cybercriminals often exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software to gain access to systems. Regular updates and patches help close these security gaps. By ensuring that all software, including operating systems and applications, is current, you reduce the risk of exploitation by attackers.
-
Employee Training and Awareness
Human error is a common cause of Cyber attacks. Regular training sessions can help employees recognize phishing attempts, suspicious links, and other common tactics used by cybercriminals. Awareness programs should be ongoing to keep security top of mind. Educating employees about the latest threats and safe online practices can significantly reduce the risk of a successful attack.
-
Use of Firewalls and Antivirus Software
Firewalls act as a barrier between your internal network and external threats, while antivirus software helps detect and remove malicious software. Both are essential components of a strong cybersecurity strategy. Firewalls monitor incoming and outgoing traffic and block unauthorized access, while antivirus software scans for and removes malware.
-
Data Encryption
Encrypting sensitive data ensures that even if it is intercepted, it cannot be read without the decryption key. This is particularly important for data transmitted over the internet and stored on devices. Encryption protects data at rest and in transit, making it more difficult for attackers to access and use the information.
-
Regular Backups
Regularly backing up data ensures that you can recover your information in the event of a cyberattack. Backups should be stored securely and tested periodically to ensure they can be restored effectively. Having reliable backups can help you quickly recover from ransomware attacks and other data loss incidents.
-
Network Segmentation
Dividing your network into segments can limit the spread of an attack. If one segment is compromised, the attacker cannot easily move to other parts of the network. Network segmentation helps contain breaches and minimizes the impact on your overall system.
-
Incident Response Plan
Having a well-defined incident response plan allows you to act quickly and effectively in the event of a cyberattack. This plan should include steps for identifying, containing, and eradicating the threat, as well as recovering from the attack. A proactive incident response plan can help minimize damage and downtime.
-
Regular Security Audits
Conducting regular security audits helps identify potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. These audits should include both internal and external assessments. Security audits provide a comprehensive review of your security posture and help you address weaknesses.
-
Secure Remote Access
With the rise of remote work, securing remote access is more important than ever. Use virtual private networks (VPNs) and ensure that remote access points are secure. VPNs encrypt remote connections, making it harder for attackers to intercept data.
How can G’Secure Labs Help?
Cyber attacks are a constant threat, evolving in parallel with technology and thus requiring multifaceted protection. In a constantly changing cyber environment, G’Secure Labs is your reliable cyber security services partner, serving you with a range of solutions and services that will secure your organization from ever-changing threats. Here’s how we can empower your defense:
Managed Detection & Response (MDR) Services
G’secure Labs offers 24/7 monitoring and response services to detect and mitigate threats in real time. Our MDR services provide a comprehensive shield against cyber threats, ensuring that your organization is protected around the clock. With advanced threat detection and rapid response capabilities, G’secure Labs helps you stay ahead of cybercriminals and cybersecurity threats.
Application Security Testing
Our proactive testing approach helps identify and counter both external and internal threats. By regularly testing applications for vulnerabilities, G’secure Labs ensures that your software remains secure against the latest threats. Application security testing helps prevent breaches and protects sensitive data from cyber security attacks.
Cyber Security Operation Center (CSOC)
G’Secure Labs operates an advanced Cyber Security Operation Centre that provides seamless protection from known and unknown cyber threats. Our CSOC is staffed by highly skilled security analysts who monitor and respond to threats in real-time. The CSOC offers continuous surveillance and rapid incident response to safeguard your assets from cybersecurity threats.
Governance, Risk Management & Compliance (GRC)
We review security policies, technical compliance, and cyber risk management posture to mitigate risks and ensure compliance with industry standards. This comprehensive approach helps organizations manage their cybersecurity risks effectively. GRC services help you maintain regulatory compliance and strengthen your security framework against cyber security attacks.
Vulnerability Assessment & Penetration Testing (VAPT)
G’Secure Labs’ VAPT services define, identify, and prioritize vulnerabilities, testing them in a controlled environment. This helps organizations understand their security weaknesses and take corrective actions before they can be exploited. VAPT services provide a thorough assessment of your security posture and actionable insights for improvement, protecting you from cybersecurity threats.
Holistic Cyber Security Services
Our 360-degree approach to cybersecurity includes a cross-technical team of security experts, including Red Team, Blue Team, and Forensics. This ensures a consolidated view of the entire security practice and lightning-fast detection and response times. Holistic services cover all aspects of cybersecurity, from prevention to incident response, safeguarding against cyber security attacks.
Industry-Specific Solution
G’Secure Labs presents cybersecurity strategies to meet the specific needs of different industries. This industry-specific approach ensures that our solutions are relevant and effective for each client. Customized solutions address the unique challenges and regulatory requirements of various sectors, protecting them from cybersecurity threats.
Strategic Alliances
We have strong relationships with leading technology vendors in the cybersecurity space. This allows us to utilize best-in-class technology and devise solutions tailored specifically to your business needs. Strategic alliances enhance the effectiveness of their cybersecurity offerings, providing strong defenses against cyber security attacks.
Commitment to Excellence
G’Secure Labs is committed to delivering high-speed, optimised, and cost-effective cybersecurity services. Our engagement models are flexible and aligned with customer needs, ensuring that they deliver the best possible outcomes. Our dedication to excellence ensures that you receive top-tier cybersecurity support, protecting you from rising cybersecurity threats.
Through G’Secure Labs, organizations can strengthen their cybersecurity posture, protect their digital assets, and ensure business continuity in the face of evolving cyber threats.